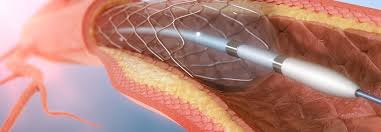
Angiography is the radiography of blood vessels by filling them with Radiocontrast agent in order to check and examine them accurately. This is a procedure for diagnosis of the interior pathology of blood vessels or Lumen. Angiography is a process that provides the most accurate information about arteries before the surgery. Using the information, the surgeon is able to treat some diseases without open surgery and if open surgery is needed, the information helps the surgeon to do it quickly and accurately. Today, diagnostic angiography is performed in an outpatient way. Firstly, the contrast agent is injected to the entrance of the vessel by a catheter inserted into arteries internal space. Then, the radiographic imaging is performed. Arteries with stenosis, aneurysm or blockage are presented in the pictures. Angiography catheter is used for examining the blood vessels in critical points of the body including the brain, kidneys, pelvis, legs, lungs, heart and legs. Doctors use this process to determine the following cases:
- Diagnosis of diseases or Aneurysms in the aorta or other large vessels
- Diagnosis of aneurysms in the aorta or other large vessels
- Diagnosis of small Aneurysm or deformed vessels around the brain
- Diagnosis of atherosclerotic disease that leads to narrowing of the arteries progressing toward the feet
- Guiding surgeons to perform reconstructive surgery on blood vessels, such as setting stent
- Diagnosis of damage in the arteries, especially in patients with brain swelling
- Diagnosis of blockages of the aorta and its main branches
- Providing appropriate plan for performing surgeries such as coronary bypass
- Identifying the exact location of internal bleeding, such as stomach ulcers
Equipment typically used for this testing includes imaging tube, X-ray tube and monitor to display the area to be tested. Angiographic catheters are similar to conventional X-ray tests. To perform this test, the nurse enters an intravenous tube through a small vein in the arm or hand. A small amount of blood may be taken before the process to ensure that kidneys work well and blood will be coagulated normally. Sometimes the painkiller is intravenously injected to reduce pain during tests. Before starting, a part of the arm where the catheter is inserted through it is well cleaned. Then the radiologist makes a very small incision on the skin so that the catheter can be inserted in the artery through it. Then the catheter is guided to the artery.
 English
English فارسی
فارسی