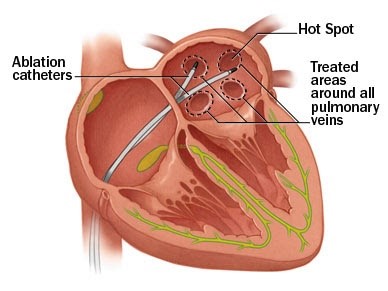
Cardiac ablation is a procedure that can correct heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias).
Cardiac ablation works by scarring or destroying tissue in your heart that triggers or sustains an abnormal heart rhythm. In some cases, cardiac ablation prevents abnormal electrical signals from entering your heart and, thus, stops the arrhythmia.
Cardiac ablation usually uses long, flexible tubes (catheters) inserted through a vein or artery in your groin and threaded to your heart to deliver energy in the form of heat or extreme cold to modify the tissues in your heart that cause an arrhythmia.
Cardiac ablation is sometimes done through open-heart surgery, but it's often done using catheters, making the procedure less invasive and shortening recovery times.
 English
English فارسی
فارسی